Tag archives for: Consulting For Architects

LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is a widely recognized and respected certification for environmentally sustainable building design and construction. Having a LEED credential can be valuable for architects and designers, as it demonstrates their knowledge and expertise in green building practices and can help them stand out in a competitive job market. Additionally, many building owners and developers are increasingly looking for professionals with LEED experience or certification, as it can help them meet their own sustainability goals and comply with local regulations. However, the value of a LEED credential may vary depending on the region and the specific market.
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certified buildings are structures that have been designed, constructed, and operated in an environmentally responsible manner. They are designed to use less energy, water, and other resources, and to produce less waste and pollution. To become LEED certified, a building must meet certain standards set by the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC), a non-profit organization that develops and maintains the LEED rating system.
LEED certification is based on a point system, with buildings earning points for meeting various sustainability criteria in categories such as energy efficiency, water efficiency, materials and resources, indoor environmental quality, and innovation in design. The building is then awarded a certification level based on the number of points earned: LEED Certified, Silver, Gold, and Platinum.
LEED certified buildings can include a variety of structures, such as office buildings, homes, schools, hospitals, retail spaces, and more. These buildings are designed to be more energy-efficient, use less water, promote better indoor air quality and reduce waste, and they provide a healthier, more productive environment for the people who use them.
There are several ways to find the best place to get LEED certified. Some steps you can take include:
- Research different training providers: Look for providers that offer LEED-specific training, have certified instructors, and provide study materials such as practice exams and flashcards.
- Look for providers with a good reputation: Check out online reviews and testimonials to get an idea of the quality of the provider’s training.
- Look for providers that offer different study options: Some providers offer in-person, online, or self-paced study options to fit your schedule.
- Check if the provider is authorized by the Green Business Certification Inc (GBCI) or other related bodies to deliver the training and the certification.
- Consider the cost and location of the training provider: Compare the costs and locations of different providers to find one that fits your budget and is convenient for you to attend.
- Look for providers that also offer continuing education hours for maintenance of the certification
It is important to keep in mind that LEED certification is a continuous process, in order to maintain the certification, the building must meet the standards of the certification level, and the certification holder must follow the continuing education requirements.
#LEED #Buildings #Certification #Certified #CBCI #USGBC #Architects #Designers
Helpful Links and Resources:
LEED Rating System
What is LEED Certification
Green Business Certification

In recent years, employees of architecture firms have increasingly attempted to join unions. This trend is driven mainly by the need for workers to protect and secure their rights as professionals. Unions provide a platform for employees to come together and negotiate fairer wages, better working conditions, and greater job security. Members can also access additional benefits such as legal advice, collective bargaining, and representation. Joining a union gives workers in the architecture field more control over their professional lives and helps to ensure that they are treated fairly and equitably by employers. As architectural firms continue to grow, the rights of employees must be protected and respected. Unions play an essential role in providing this protection, giving individuals the peace of mind that their rights and interests are protected.
By joining a union, architecture firm employees can help improve the industry. By negotiating better wages and working conditions, they can ensure that every professional in the field is treated fairly and compensated equitably for their work. The collective strength of union members also allows them to speak out against any injustices or exploitative practices they may experience, ensuring that their voices are heard and respected. With more people joining unions, the architecture industry is becoming safer and fairer for everyone involved.
Overall, union membership offers a range of benefits for employees in the architecture field. It gives them a platform to fight for their rights, negotiate better wages and working conditions, and ensure their voices are heard. By joining a union, they can help create a fairer and more equitable industry for everyone involved. As the architecture field continues to evolve, unions will remain essential to ensuring that workers’ rights are respected. But is it fools gold?
As architecture firm owners consider the implications of unionization, they must weigh the risks and rewards. Unionized firms face higher costs for labor, resulting in increased overhead that diminishes their competitive edge. Furthermore, collective bargaining agreements can restrict a firm’s ability to manage staffing levels and set salaries according to market conditions. Not being nimble can limit a firm’s ability to adapt quickly to changes in the industry, as well as its ability to attract and retain talented employees. Ultimately, these factors make unionization a less attractive option for many architecture firm owners. However, it is important to note that unions can bring tangible benefits, such as job security and improved wages and working conditions, which could appeal to some. Ultimately, it is up to individual owners to decide if unionization is the right choice for their businesses.
Architects are held to a high standard due to the critical nature of their work. They must possess excellent technical knowledge and communicate effectively with clients, designers, and contractors. As a result, they often require specialized training or certification to practice as professional architects. Despite this need for advanced skills and rigorous qualifications, architects are usually not eligible for collective bargaining, as many operate independently or in small firms and do not form unions. Thus, architects must advocate for their interests regarding workplace issues such as wages and working conditions. Architects must be aware of their rights and understand the profession’s regulations to ensure they receive fair compensation and working conditions. By doing so, architects can ensure they can continue practicing their craft in a healthy and productive environment.
Although architects traditionally do not form unions, they should still be aware of their rights and participate in the industry conversation around workplace issues. By doing so, architects can ensure they are compensated fairly and work in environments that promote their skillset and creativity. Architects must understand how their profession can benefit from unionization to better advocate for their interests.
It isn’t easy to find accurate statistics on how many architecture firms are unionized, as most are privately owned. However, there have been reports that suggest that under 3% of all architecture firms in the world and one firm in the United States may be part of a union or labor association.
Although becoming part of a union offers specific employee benefits, such as increased bargaining power and better wages, it can also be limiting in terms of flexibility. By joining a union, an architectural firm is subject to “just cause” guidelines regarding hiring and firing. Just cause means that there must be documented evidence that an employee is not meeting the standards of their position or has committed a punishable offense before they can be terminated. Therefore, it is complicated for an architectural firm to manage its workload most efficiently, as there may not be the flexibility to let go of employees quickly during times of low demand. Additionally, unions can restrict how many subcontractors or temporary workers an architecture firm can hire at any given time, limiting their ability to adapt to changing needs. Including dictating the workflow in contrast to increasing/decreasing staffing levels as needed. In addition, unions are not typically supportive of “at will” employment, which provides much more flexibility when hiring and firing.
Overall, unions can provide many benefits to architectural firms but also have certain restrictions that must be weighed carefully. Architecture firms must consider all their options before deciding on joining or not joining a union. Ultimately, the best solution will depend on each firm’s specific needs and goals.
For architecture firms that decide to join a union, there are measures they can take to ensure the best outcomes for their business. For example, firms should make sure they familiarize themselves with the rules and regulations of the union and negotiate any hiring or firing restrictions to ensure maximum flexibility when managing staff levels. Additionally, it is vital to understand the union’s grievance process and how disputes will be handled. Finally, firms should also consider creating a separate contract with the union that outlines their expectations for staffing levels and hiring and firing procedures.
By taking these measures, architectural firms can ensure that joining a union does not limit their ability to perform their work efficiently and effectively.
This information is for educational purposes and does not constitute financial, legal, or other professional advice. Please consult with a qualified professional if you require assistance.
Additional resources:
– New York Times: https://www.nytimes.com/2021/12/21/business/architects-white-collar-union.html
– The Real Deal: https://therealdeal.com/2022/09/01/new-york-firm-establishes-architectures-first-union/
– Architects’ Journal: https://www.architectsjournal.co.uk/news/do-architects-need-a-trade-union
– National Labor Relations Board (NLRB): https://www.nlrb.gov/
– American Institute of Architects (AIA): https://info.aia.org/join-aia/collective-bargaining-labor
– National Association of Architects (NAA): http://www.naahq.org/
– American Federation of Architects and Engineers: https://afae.org/
– Society of Professional & Executive Employers (SPEE): http://speeusa.org/
– U.S. Department of Labor: https://www.dol.gov/general/topic/labor-relations/labor-unions
– American Bar Association: https://www.americanbar.org/groups/labor_law/publications/aba_books/unionbargaining.html
– Harvard Law School: https://www.law.harvard.edu/news/labour/collective-bargaining-and-labor-unions/
– Cornell Law School: https://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/labor_union
– Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS): https://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/2011/ted_20110429_data.htm
– Governing: https://www.governing.com/topics/workforce/unionizing-workers-collective-bargaining-rights.html
– National Labor Relations Board (NLRB): https://www.nlrb.gov/what-we-do/protecting-employee
Architecture Practice
|
architects, architecture, atwill, collectivebarganing, Consulting For Architects, David McFadden, design, firing, Hiring, jobs, Jobsecurity, justcause, salary, Trade, Unions, wages, workingconditions
|
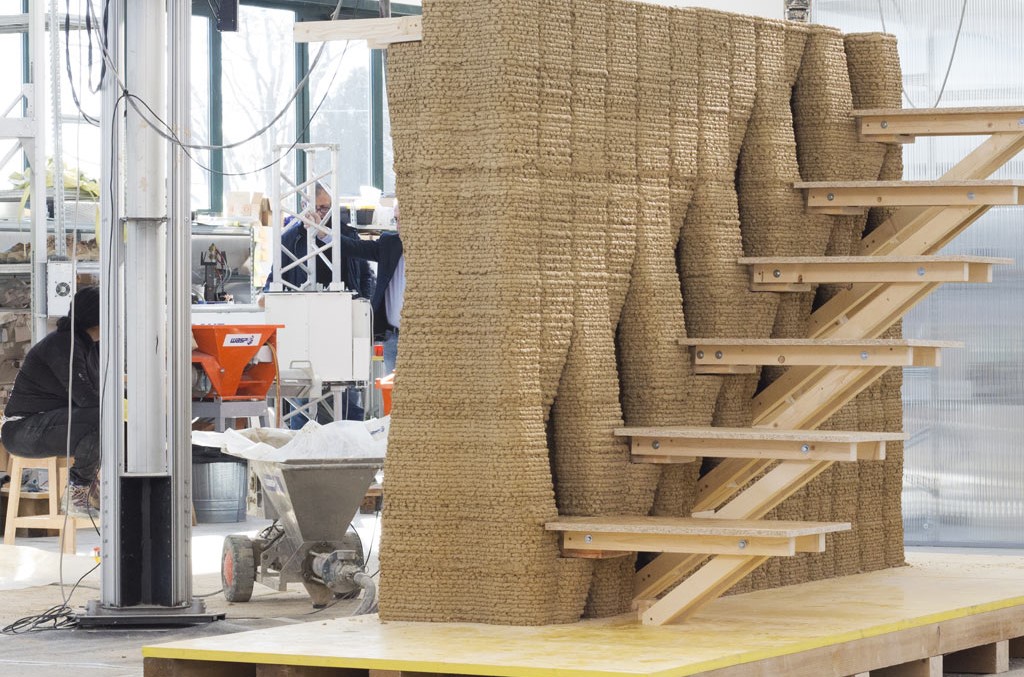

3D printing is revolutionizing the field of architecture, and it is poised to change the way we build our cities and towns in the future. Thanks to this innovative technology, we will be able to create more sustainable, resilient, and beautiful buildings than ever before.
In recent years, 3D printing has become increasingly popular, and it is now used in various industries. One area where 3D printing is making a significant impact is architecture. This technology offers several advantages for architects, including creating complex shapes and structures that would be impossible to create using traditional methods. 3D printing also allows for a high degree of customization, meaning that each architectural element can be designed to meet the project’s specific needs.
So how does 3D printing work in architecture? First, architects create a digital model of the desired structure using specialized software. Once the model is complete, it is sent to a 3D printer. The printer then creates the structure by building it up layer by layer, using materials such as plastic, metal, or concrete. This process can take anywhere from a few hours to several days, depending on the size and complexity of the project.
As anyone who has tried to put together a model kit can attest, 3D printing can be a great way to create complex shapes with high accuracy. Some of the world’s leading architecture firms are now using 3D printing to create scaled models of their proposed designs. Not only does this allow for greater precision in the planning stages, but it also allows for modifications to be made quickly and easily. In addition, using 3D printing means that architecture, engineering, and construction firms can create full-sized prototypes of their designs, which can be used to test the feasibility and identify any potential problems. As 3D printing technology advances, we will likely see more and more firms incorporating it into their design practices.
Several universities are now offering courses in 3D printing for architects. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in 3D printing among architects and other design professionals. As a result, several universities are now offering courses in this technology. These courses typically cover the basics of 3D printing, such as creating digital models and operating a 3D printer. In addition, students are often allowed to design and print their projects. These courses provide a great introduction to this exciting technology and its potential applications in architecture.
3D printing is set to change the way we build our cities. There is no doubt that 3D printing is a disruptive technology set to change how we build our cities. This technology offers several advantages for architects, including creating complex shapes and structures that would be impossible to create using traditional methods. In addition, 3D printing allows for a high degree of customization, meaning that each architectural element can be designed to meet the project’s specific needs. As the use of 3D printing technology continues to grow, we will likely see several innovative and exciting projects that push the boundaries of what is possible.
3D printing is a process that is constantly evolving and has the potential to change the landscape of architectural design. While there are some disadvantages to using this technology, the advantages often outweigh them. With continued advancement in 3D printing technology, we can only imagine what possibilities will be made available for architects and their clients. What do you think the future of 3D printing holds for architecture? Let us know in the comments below!
Related:
10 of the Best 3D Printers for Architects in 2022 Reviewed | Top Brands Compared
Reservations Begin in 2023 for the 100-home Community Codesigned by BIG-Bjarke Ingels Group
LGM turns to Quickparts for on-demand architectural modeling
Architecture Practice
|
3dmodel, 3dprinting, 3dsoftware, architects, architecture, Construction, Consulting For Architects, David McFadden, design, digital, Engineering, jobs, model, project, technology
|

What started as a comment has become a short post in response to an opinion article by Adam Greenfield in the current edition of Dezeen online titled “All those complicit in Neom’s design and construction are already destroyers of worlds.”
In Sum.
• Adam Greenfield’s opinion article titled “All those complicit in Neom’s design and construction are already destroyers of worlds” argues that anyone who accepts money to work on any aspect of the Neom project is automatically complicit in everything that the project does.
• I disagree with this opinion. I believe that everyone is responsible for choosing which parts they work on and to what extent. If they are not comfortable with a particular aspect of the project, they can always decline to work on it or limit their involvement.
• Architecture is often seen as a symbol of power and authority, but it can also be seen as a reflection of the political and economic ideologies of the society in which it is built. In some cases, architecture may even help to shape these ideologies.
• The author paints architects who accept commissions with a broad brush when reality shows that many architects are conscious of ethical implications in their projects.
I disagree that if you accept money to work on any aspect of the Neom project, you need to know that you are complicit. I believe in and support many parts of the project, and I would gladly accept compensation for my work on those aspects. I do not think that taking money makes me automatically complicit in everything that the project does; it is my responsibility to choose which parts I work on and to what extent. If I am not comfortable with a particular aspect of the project, I can always decline to work on it or limit my involvement. Ultimately, it is up to each individual to decide whether or not they want to accept money to work on the Neom.
Architecture is often seen as a symbol of power and authority. This is especially true of traditional, classical architecture, which is often associated with authoritarian regimes such as the Roman Empire or the British monarchy. However, architecture is also drawn to capitalist and socialist governments. In capitalist societies, architecture is often seen as a way to make money and attract investment. In contrast, in socialist societies, it is seen as a way to improve the lives of citizens and promote equality.
Architecture can therefore be seen as a reflection of the political and economic ideologies of the society in which it is built. In some cases, architecture may even help to shape these ideologies. For example, the Bauhaus design school was founded in Germany in the 1920s to combine art and industry. This was when the country was undergoing a period of political and economic change, and the Bauhaus school helped shape the new German identity. Similarly, post-modern architecture emerged in the 1970s as a reaction to the modernist movement dominating architecture.
Noem’s cutting-edge Line project is about new tech and inventions to tackle global warming, setting a new benchmark for future urban cities. The developers and architects are a small part of the project team, which includes futurists, scientists, inventors, engineers, and artists. Their innovative approach means that the line project will not contribute to global warming but instead help fight it. This is a crucial step in the right direction. The Neom team is passionate about making a difference and ensuring that our planet has a bright future. We believe that through technology and innovation, we can make this happen.
The author paints the architects that accept commissions with a broad brush when the reality is much more nuanced. As such, it is essential to consider the ethical implications of their work. This includes whether or not they are contributing to the displacement of indigenous peoples or exacerbating climate change.
While it is easy to paint all architects and the commissions they earn with a broad brush, the reality is much more nuanced. Many architects are conscious of the ethical implications of their work and make an effort to minimize the negative impact of their projects.
It is essential to hold all architects accountable for the societal implications of their work. But it is also important to remember that not all architects are the same. Some are working to make a positive difference in the world. Knowing that sitting on the sidelines affects nothing Morphosis, Zaha Hadid Architects and other studios committed to the Neom project can sleep well tonight.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
After working at various design practices on a full-time and freelance basis and starting his design firm, David McFadden saw a gap to fill in the industry. In 1984, he created an expansive hub for architects and hiring firms to sync up, complete projects, and mutually benefit. That hub was Consulting For Architects Inc., which enabled architects to find meaningful design work while freeing hiring firms from tedious hiring-firing cycles. This departure from the traditional, more rigid style of employer-employee relations was just what the industry needed – flexibility and adaption to current work circumstances. David has successfully advised his clients and staff through the trials and tribulations of four recessions – the early ’80s, the early ’90s, the early 2000s, the Great Recession of 2007, and the Pandemic.
Op-Ed
|
AdamGreenfield, AllthosecomplicitinNeomsdesignandconstructionarealreadydestroyersofworlds, architects, architecture, bauhaus, business, cities, Consulting For Architects, David McFadden, design, dezeen, futurists, globalwarming, jobs, Line, Morphosis, Noem, Saudi, urban, zahahadid
|

As the gig economy continues to grow, so do the number of questions about how the law will be regulated. President Biden’s proposed legislation, the Protecting the Right to Organize (PRO) Act, includes several provisions that could significantly impact gig workers, including freelance architects and interior designers.
The PRO Act would make it easier for gig workers to unionize by clarifying that they are employees, not independent contractors. It would also give them the right to bargain collectively with their employers.
The bill would also make it illegal for companies to misclassify their workers as independent contractors to avoid paying benefits or complying with labor laws, even in cases where the worker is an independent contractor and prefers to work that way.
Working as an independent contractor has many benefits for architects and interior designers. These professionals can enjoy greater control over their work, schedule, and income. Additionally, they are not tied to one company or location and can take on projects that interest them from anywhere in the world. Independent contractors often have more freedom to negotiate fees and choose their working hours. They also typically have lower overhead costs than traditional businesses, which results in higher profits. In addition, they are not subject to the same employment laws and regulations as conventional businesses, giving them more flexibility in operating.
If you believe every worker in America should be the employee of a firm rather than work for themselves, you should support the passage of the PRO Act. If not, there are a few things that architects and interior designers can do to fight the passage of this law. First, they can educate themselves and others about the potential negative impacts of the law. Second, they can contact their local representatives and let them know their concerns. Finally, they can support organizations fighting against the passage of the law. Where do our professional associations stand? Contact the national headquarters of The American Institute of Architects and work with them to develop a strategy. https://www.aia.org/pages/6347502-federal-advocacy-outreach.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
After working at various design practices on a full-time and freelance basis and starting his design firm, David McFadden saw a gap to fill in the industry. In 1984, he created an expansive hub for architects and hiring firms to sync up, complete projects, and mutually benefit. That hub was Consulting For Architects Inc., which enabled architects to find meaningful design work while freeing hiring firms from tedious hiring-firing cycles. This departure from the traditional, more rigid style of employer-employee relations was just what the industry needed – flexibility and adaption to current work circumstances. David has successfully advised his clients and staff through the trials and tribulations of four recessions – the early ’80s, the early ’90s, the early 2000s, the Great Recession of 2007, and the Pandemic.
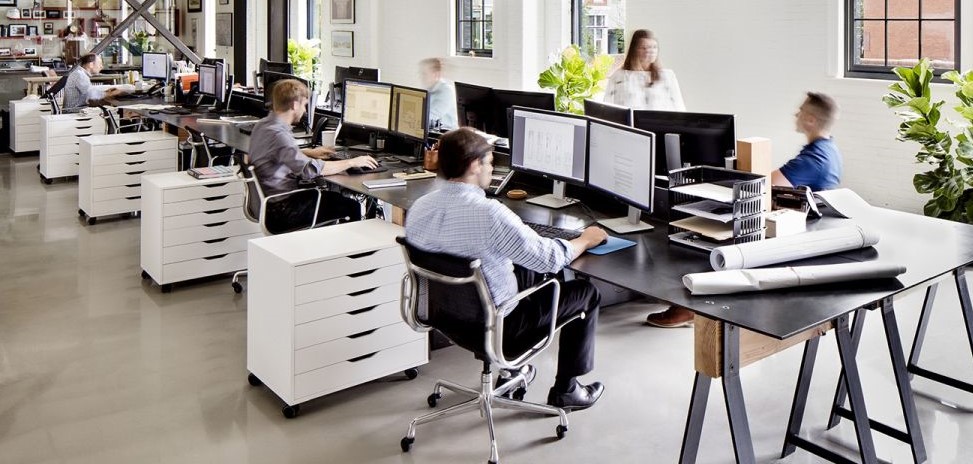

Flex-core staffing is an excellent way for architecture firms to break the hiring-firing cycle, increase their firm’s bottom line, and keep their employees happy. By hiring temp architects to fill in the peaks and valleys that always occur, firms can keep their core staff intact and avoid the need to engage and fire employees constantly. This practice can save firms both time and money, and it can also help them maintain a higher level of quality control.
Few things are more costly to a business than the hiring and firing cycle. Not only does it take a toll on your human resources department, but it can also significantly impact your bottom line.
Fortunately, there are ways to break the cycle and improve your financial situation. You can improve your bottom line and increase profits by taking some simple steps.
1. Review your hiring practices. Poor hiring practices are the most common causes of the hiring and firing cycle. If you’re constantly hiring and then firing employees, it’s time to take a closer look at your process. Are you screening applicants properly? Are you asking the right questions?
2. Train your managers. Another common cause of the hiring and firing cycle is poor management. If your managers constantly have to deal with employee issues, it’s time to give them some training. Teach them how to manage their teams and handle conflict appropriately.
3. Communicate with your employees. One of the best ways to avoid the hiring and firing cycle is to communicate with your employees. Let them know what your expectations are, and give them regular feedback. This will help them understand what they need to do to meet your standards.
4. Be consistent with your policies. You must comply with your policies to avoid the hiring and firing cycle. Make sure that everyone in your company knows your procedures and that they are followed. This will help to create a sense of stability and reduce the need for turnover.
5. Offer incentives. Another great way to avoid the hiring and firing cycle is to offer incentives for good performance. If you have employees who consistently meet or exceed your expectations, offer them a bonus or other incentive. This will show them you’re serious about their work and appreciate their efforts.
These simple steps can break the hiring and firing cycle and improve your bottom line. Implement these tips in your business today and see the difference it makes.
There are many ways to increase an architecture firm’s bottom line. One way is to increase the number of projects that the firm takes on. Another way is to increase the fees that the firm charges. Still, another method is to cut costs.
One way to increase an architecture firm’s bottom line is to increase the number of projects that the firm takes on. This can be done by marketing the firm more aggressively or by expanding the geographic areas that the firm serves.
Another way to increase an architecture firm’s bottom line is to increase the fees that the firm charges. This can be done by expanding the firm’s service rates or adding new services that command higher fees.
Still another way to increase an architecture firm’s bottom line is to cut costs. This can be done by streamlining the firm’s operations, eliminating unnecessary expenses, or finding ways to save on materials and labor.
Increasing an architecture firm’s bottom line can have many benefits. It can improve the firm’s financial health, allow the firm to hire more staff, and enable the firm to expand its services. Taking steps to increase an architecture firm’s bottom line can help the firm become more prosperous.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
After working at various design practices on a full-time and freelance basis and starting his design firm, David McFadden saw a gap to fill in the industry. In 1984, he created an expansive hub for architects and hiring firms to sync up, complete projects, and mutually benefit. That hub was Consulting For Architects Inc., which enabled architects to find meaningful design work while freeing hiring firms from tedious hiring-firing cycles. This departure from the traditional, more rigid style of employer-employee relations was just what the industry needed – flexibility and adaption to current work circumstances. David has successfully advised his clients and staff through the trials and tribulations of four recessions – the early ’80s, the early ’90s, the early 2000s, the Great Recession of 2007, and the Pandemic.
Hiring trends
|
architects, architecture, business, Consulting For Architects, design, employees, firing, firms, flex, Hiring, human, Interviewing, jobs, Labor Market, manage, porfolio, resources, resume, screening, staffing
|

There are always peaks and valleys in the work of an architectural firm. Sometimes we work on multiple projects at different phases. Other times we are focused on a single project. Design Development and Construction Documents phases can be exceptionally hectic, with deadlines looming.
There are many reasons to pursue a career as an architect on a project basis. Perhaps you are looking for a way to accelerate your career growth, or you want to avoid pigeonholing into one particular type of architecture. Either way, working on back-to-back projects at different firms can give you the necessary experience to be more marketable than your peer group.
Most architects begin their careers working at one firm for several years. However, there are many benefits to pursuing a career as an architect on a temporary or project basis. Here are just a few:
1. You will gain experience working on a variety of different types of projects.
2. You will have the opportunity to work at different firms, each with a unique culture and approach to architecture.
3. You will be able to build a network of contacts across the industry.
4. You will develop a more marketable portfolio because of your diverse experience.
Job Seekers
CFA is a full-service placement and recruiting firm. Our recruiters will help you find the perfect new job and career. We work with top companies in various industries and can connect you with opportunities that best match your skillset and goals. Whether you’re looking for a new challenge, higher compensation, better use of your skillset, growth potential, or a better work/life balance, CFA can help you find the right fit for your design sensibilities.
If you’re passively searching or already in the job market, submit your resume today, and one of our experienced recruiters will reach out to discuss available opportunities.
CFA also offers various other services to job seekers, including resume writing, interview coaching, and salary negotiation assistance. We can help you at every step of your job search, from finding the right opportunity to nailing the interview and negotiating the best possible salary.
CFA quickly became the industry leader in flexible hiring, full-time freelancing, and project consulting. Our years of experience and commitment to quality have made us the go-to source for architecture and interior design talent. We offer a wide range of services to meet the needs of our clients, and our team of experts is always available to help you find the right solution for your project.
Since its founding, CFA has helped thousands of architects and interior designers find their ideal job placements. We take pride in our reputation as one of the industry’s most respected and trusted names.
If you’re looking for a trusted partner to help you with your next project, look no further than CFA. We have the knowledge and experience to get the job done right, and we’re always here to help you find the perfect solution for your needs. Contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can help you succeed at 212-532-4360 or email your resume and portfolio to recruiters @ cons4arch. com
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
After working at various design practices on a full-time and freelance basis and starting his design firm, David McFadden saw a gap to fill in the industry. In 1984, he created an expansive hub for architects and hiring firms to sync up, complete projects, and mutually benefit. That hub was Consulting For Architects Inc., which enabled architects to find meaningful design work while freeing hiring firms from tedious hiring-firing cycles. This departure from the traditional, more rigid style of employer-employee relations was just what the industry needed – flexibility and adaption to current work circumstances. David has successfully advised his clients and staff through the trials and tribulations of four recessions – the early ’80s, the early ’90s, the early 2000s, the Great Recession of 2007, and the Pandemic.
Project Based Work
|
architects, architecture, Careers, Consulting For Architects, flexible, freelancing, Interviewing, jobs, opportunities, pandemic, Project based, recruiters, resume, salary, workforce, worklifebalance, writing
|

October 6, 2022 – The post-pandemic job hunt is in full swing, and for architects and interior designers, the demand is higher than the supply. With businesses reopening and new companies starting, there is a greater need for these professionals’ design services. If you are an architect or interior designer looking for a job, now is the time to start your search!
There are a few things that you can do to increase your chances of landing the job that you want. First, ensure that your resume and portfolio are up-to-date and highlight your experience in the industry. Next, reach out to your contacts and let them know you are looking for work. Don’t be afraid to apply for jobs outside your usual area of expertise; sometimes, the best opportunities come from unexpected places. Seek out a salary and compensation package that takes inflation into account. And finally, enlist a qualified placement firm on your behalf to uncover “hidden” openings.
With a little effort, you should be able to find the perfect job in this post-pandemic world. Good luck!
Do you have any tips for job hunting in the current market? Could you share them with us in the comments?
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
After working at various design practices on a full-time and freelance basis and starting his design firm, David McFadden saw a gap to fill in the industry. In 1984, he created an expansive hub for architects and hiring firms to sync up, complete projects, and mutually benefit. That hub was Consulting For Architects Inc., which enabled architects to find meaningful design work while freeing hiring firms from tedious hiring-firing cycles. This departure from the traditional, more rigid style of employer-employee relations was just what the industry needed – flexibility and adaption to current work circumstances. David has successfully advised his clients and staff through the trials and tribulations of four recessions – the early ’80s, the early ’90s, the early 2000s, the Great Recession of 2007, and the Pandemic.
The Job Hunt
|
architects, architecture, Consulting For Architects, David McFadden, demand, design, interiordesigners, jobhunt, jobs, pandemic, post, resume, supply, talent, Talent Shortage, unemployed architects
|
December 7, 2021 – Freelancers and Independent Contractors Beware: Build Back Better Vows to Impose the PRO Act Which Threatens Your Livelihood
The freedom to work as a freelancer or independent contractor provides flexibility for households and vibrancy to the American economy. It is tailor-made for architecture and design practices and freelance architects seeking to fill the peaks and valleys standard in architecture practices.
The PRO Act bans Right to Work laws nationwide. Still, it also imposes the same independent contractor/freelancer-destroying policies of California’s AB5 law, which has destroyed countless lives and driven people out of the Golden State.
Freelancers and independent contractors want to be their bosses. AB5 and the PRO Act dictate they must have a boss. Households need greater flexibility than ever after the changes brought about by COVID in the workplace.
I have been fighting my whole professional career for the right to freelance and become an independent contractor. We need to rally the political wing of AIA.org and ask their Advocacy group to engage and lobby against this provision of the Build Back Better bill.
Act Now Contact Sarah Dodge, AIA, Senior Vice-President of Advocacy & Relationships, and ask her to put the full force of the AIA’s advocacy group behind removing the AB5 provision out of Build Back Better!
[email protected]
Partial hat tip to the Freelancers Union
Freelance Community
|
AB5 Law, AIA.org, American Institute of Architects, architects, architecture, architecture practices, Build Back Better, Consulting For Architects, COVID, David McFadden, design, economy, Freelancers, freelancing, Independent Contractors, jobs, Livelihood, Pro Act, Workplace
|

In our third installment of Archinect’s Guide to Job Titles series, we attempt to tackle the nuanced role of the Studio Director without falling back on search engines like Google and Bing or job boards like Glassdoor, Indeed, Monster, or Ladders [not in original article]. As with most positions within architecture firms, the lines are quite blurry when it comes to the role of Studio Director. For some, this leadership position acts as a kind of operations specialist and strategist while also functioning as a firmwide design leader. For others, the Studio Director might function as a buffer between design teams and the higher-level leadership of an organization. And for others still, this individual might run their studio as a kind of “mini-firm” within a larger firm, responsible for their own business development, hiring, project management, and overall growth. The intricacies and variations associated with such a dynamic posting can’t be explained exhaustively, there will always be some deviation. Nevertheless, what follows is our attempt to capture the inherent essence of this career path in architecture.
Structural Relevance
Architecture firms come in many forms. Depending on size, the internal structure of the personnel will differ. Some firms might operate in a departmental structure, where each team works on a specific phase of a project: a design “department” might work on the programming and schematic phases before passing the work on to a technical department that would realize the construction documentation. Others might have various project teams, each with its own project managers who are overseen by a Studio Director or Principal(s). And others still might divide into multiple studios, each with a specific function, and led by their own Studio Director, respectively. In this structure, each Studio Director would report to a Managing Principal, Design Principal, or both. Some Studio Directors may even be partners of the firm or Principals themselves. When it comes to the possible organizational structures of design firms, the variations are many.
While the interpretation of the role will differ from office to office, a Studio Director will typically oversee a studio. This may be a single studio under one roof, with a small or medium-sized staff, separated into smaller teams, each with a project architect/project manager, a job captain, and designers. Each team leader could report to a Studio Director who then might report to or collaborate with a higher-level leadership team, such as a firm’s Principal(s).
A studio could also be one of many within a larger firm, each with an expertise focus such as hospitality, healthcare, sports, workplace, restoration, or interiors. Each Studio Director would have specialized knowledge and experience in their area of expertise. In this model, studios might operate under the umbrella of a larger firm but would function as its own “sub-firm,” having its own clients, staff, and sometimes even its own receptionist. These “studio structures” can vary widely, and the nuances will depend on the organization in question.
A Studio Director Needs to be a People Person
In Archinect’s Growing Leadership and Practice: Laney LA’s Search for a Studio Director, we dove deep into conversation with Anthony Laney of Laney LA about his search for a Studio Director. “On day one, five project managers, each with their own team of one to two aspiring architects, will report to the Studio Director,” Laney told Archinect. “So, in total, the Studio Director will be leading a team of about 14 people. Right now, I’m giving about 30 percent of my time to a Studio Director role. We want to tear the lid off of that and allow someone to give it 100 percent of their time.” Here we have the leader of a relatively medium-sized firm in need of a Studio Director to act as a point person between him and his project managers. Laney saw this as someone who was not only in love with design, but who also had a deep passion for creating and building a great team.
People skills are 80 percent of the job, probably more…
Archinect also spoke with Lindsay Green, Principal and Studio Director at OFFICEUNTITLED, and Shawn Gehle, Principal and Co-Founder. On the topic of managing a team and dealing with different kinds of people, the pair elaborated further. “People skills are 80 percent of the job, probably more,” they said. “You have to deal with multiple personalities every day. Happy people; sad people; staff; clients; personal issues amongst the team.” They went on to articulate the expansive role a Studio Director might have within an office. In addition to effectively managing people, a leader in this role might also take on responsibilities of reviewing the office’s backlog and ensuring future staffing needs are fulfilled, overall professional development and client management, internal development of team members, human resources, and finance. “We really rely on Lindsay to run this office, we look to her to understand our overall health and outlook,” Gehle said of Green. “She acts as a kind of Chief Operations Officer, shepherding the resources within the office.”
A Strong Business Acumen
Green’s role goes far beyond that of the traditional project manager or project architect, but rises further into rigorous strategic planning and execution, calling for business acumen and facility not typical in architects. “I think if someone is considering this role as something to work towards in their career, they should consider getting an MBA. Understanding business is crucial in this position,” Green elaborated. “And even after that, it’ll take on-the-job experience to establish an understanding of how firms operate.”
Where before one’s core preoccupation might have been client satisfaction, design quality, timely deliverables, and internal team health, the focus now expands to a broader higher level concentration dealing with the business, strategic, and developmental aspects of the organization as a whole. Yes, project teams are concerned with these aspects, but on a fundamentally different level. They have a responsibility for their projects, whereas a Studio Director’s daily duties directly deal with the trajectory and direction of the bigger picture, moving beyond a partial focus to a comprehensive one.
What are firms looking for?
So what are firms looking for in a Studio Director? Take Gensler, a corporation based around a “collaborative studio leadership model.” Each studio has a specialty and is led by a highly experienced Studio Director, who oversees everything from overall management of the team and projects to the finances and budget. They work closely with staff in both professional development and mentorship as well as hiring in collaboration with HR. Studio Directors at Gensler are responsible for marketing, developing new business, and responding to RFPs, along with several other high-level responsibilities. According to Gensler, those pursuing this role should have a minimum of 15 years of experience and have a proven record in their area of focus. Moreover, Studio Directors at Gensler should possess a comprehensive personal portfolio of work, illustrating their aptitude and understanding of their expertise. Essentially, Studio Directors are leaders of their own small firm within the larger organization that is Gensler.
A Multi-Disciplined Leader
In the end, Studio Directors are multi-disciplined leaders with a depth of experience that allows them to lead a team of professionals of varying experience levels. They operate on multiple fronts, some of which include business functions such as staff development, hiring, strategic planning, finances, as well as traditional functions like QAQC, guiding design quality, and managing clients and projects. The possibilities appear broad and wide-ranging, but we’ve learned that business acumen is crucial, people skills are essential, and a deep understanding of the traditional functions of the architect, indispensable.
Author – Sean Joyner is an architect-trained writer and editor at Archinect. His articles and essays utilize themes in history, philosophy, and psychology to explore lessons for students and professionals within the fields of architecture and design. Sean’s work prior to Archinect focused primarily on k-12 and higher education projects in Southern California. Some of the things Sean enjoys are playing and practicing chess, studying obscure topics like quantum physics and cryptography, working out, and reading compelling books.
Sean Joyner’s Blog on Archinect
Archinect
Consulting For Architects, Inc. Staffing and Recruiting Hiring Trends Blog
Articles:
Salary and responsibilities for design directors for interior design
Harvard GSD announces winners of 2020 Richard Rogers Fellowship
Job Titles
|
Archinect, architecture, architecture jobs, Careers, Consulting For Architects, design, Gensler, Hiring, hiring an architect, hiring firms, ilookup, jobs, mentoring, studio, studio director, teaching, titles
|

















